Remote SDR v2 – Orange Pi One Plus or Orange Pi Zero 2 image installation

Below is the detailed procedure to install Remote SDR in version 2 on an Orange Pi One Plus or an Orange Pi Zero 2. The latest images written on a 32 GB SD card, are available on Github. They are different for each of the SBC.
https://github.com/F1ATB/Remote-SDR/releases
Note: it seems that as of this day (July 2021), the Orange pi One Plus is no longer on sale. On the other hand, the Orange Pi Zero 2 remains available.

Note that all the 32GB SD card have not exactly the same size. The image proposed here has been prepared on a small one. I hope it will cover all needs.
Remote SDR V2 – Improvements
Remote SDR is an application allowing remote control from a web browser, a radio transceiver based around 1 or 2 SDR (Software Design Radio).
The Orange Pi One Plus is a “Single Board Computer” card which, thanks to a 4-core 64-bit processor, provides the computing power necessary for signal processing at a cost of less than 40 €. The Orange Pi Zero 2, a recent SBC (Single Board Computer) additionally provided with WIFI access. The main changes brought by this new version of Remote SDR are:
- Adalm-Pluto SDR compatibility in addition to HackRF One and RTL-SDR
- Reception in NBFM, WBFM, AM in addition to SSB
- Emission in NBFM or SSB with Pluto or HackRF One
- Reception spectrum on 2048 FFT points instead of 1024
- Supply of system and SDR observation tools
The latest version v2.1 (May 2021) improves Remote SDR when used with a smartphone.
Image installation for Orange PI One Plus
- Download the image on Github
https://github.com/F1ATB/Remote-SDR/releases - Unzip the image
- Write image to 32GB micro SD card with PC software like Win32diskmanager
- Connect a Pluto, HackRF One or RTL-SDR SDR
- Connect the Orange Pi to the local ethernet network
- Power up the Orange Pi
- Go to your internet box to find the IP address that has been assigned to the Orange Pi
Launch of Remote SDR v2
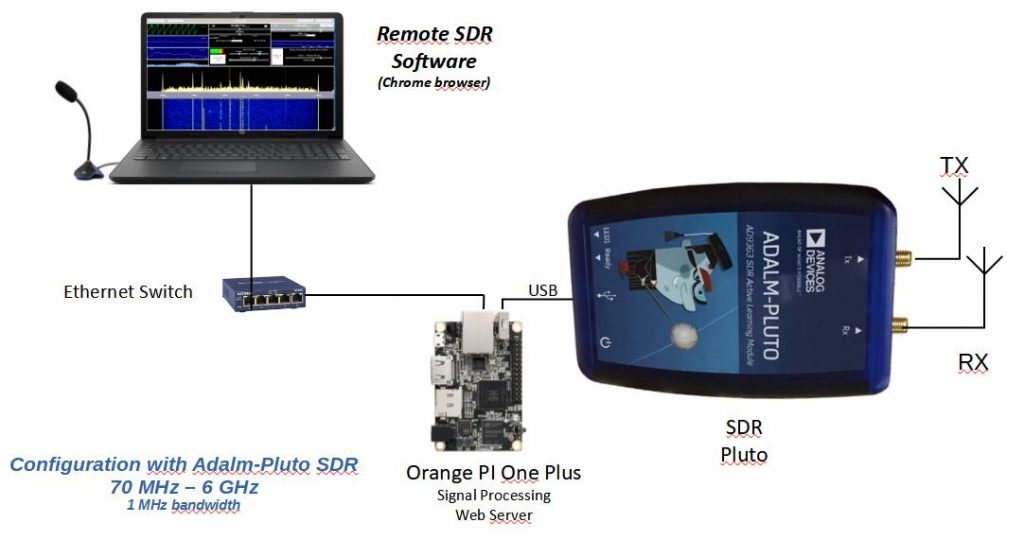
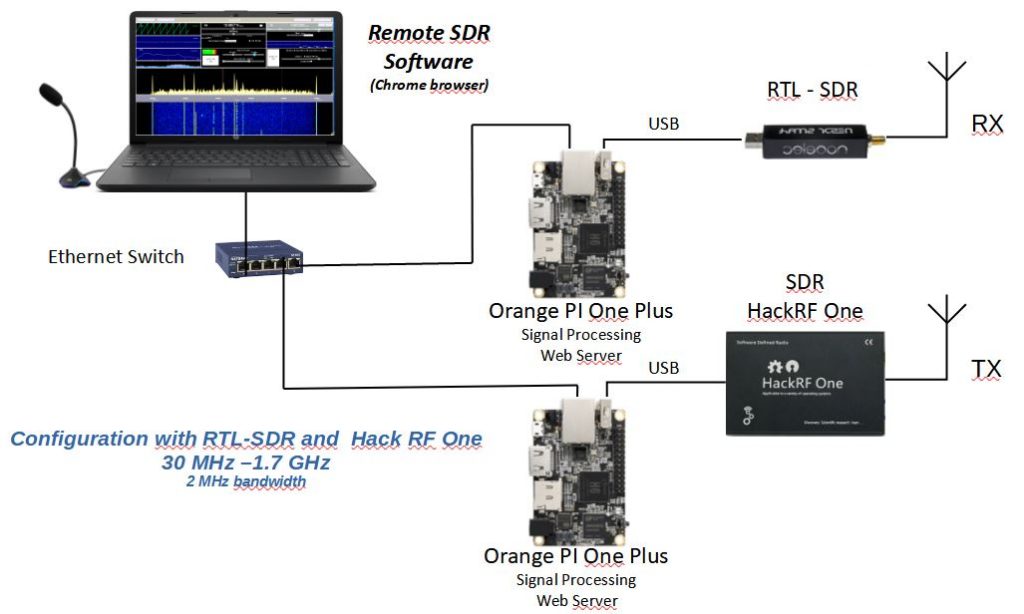
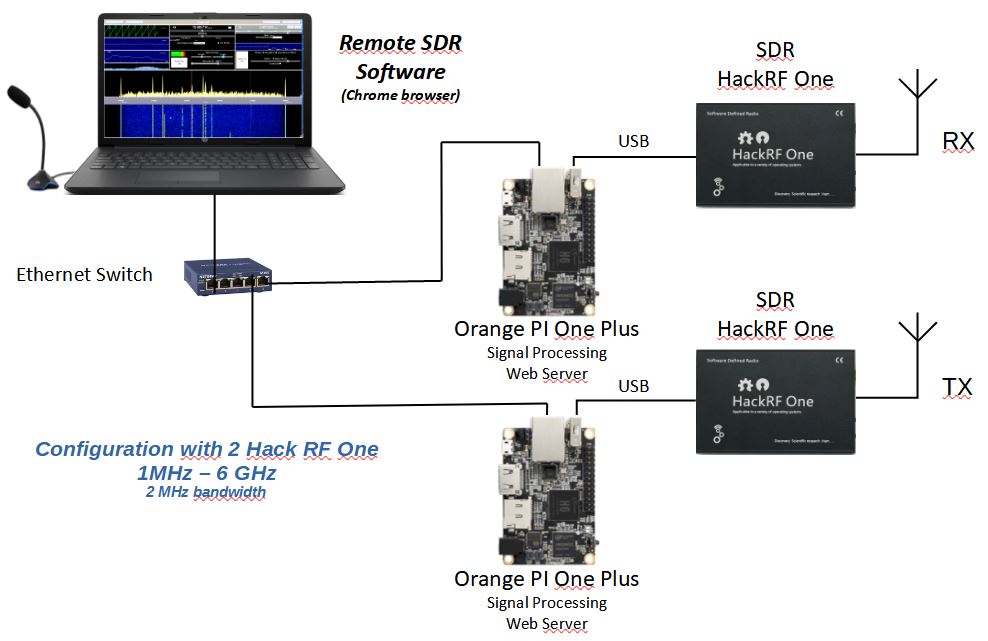
If you are using an Adalm-Pluto, only one Orange PI is needed. If you use a HackRF in transmission and an RTL-SDR or hackRF in reception, you will need 2 Orange Pi with the same configuration. You launch the application on one of the Orange PIs at the address:
http://<ip de l’orange pi>
Note that an USB Hub is needed between the Pluto and the Orange PI. It’s a system bug.
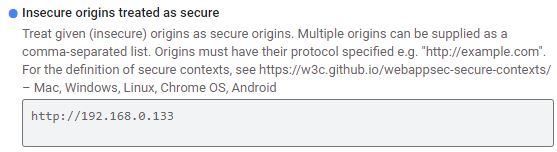
You need a modern browser like Chrome or Edge. These do not give access to the microphone if the site does not have secure access in https. On your local network at home, you generally work in http simply. To get around this difficulty, the solution is to set up a derogation at the level of the web browser by accessing the “flags” parameters. you must type in the address bar:
with Chrome: chrome://flags
with Edge(2020): edge://flags
Look for the header:
Insecure origins treated as secure
Fill in the field as below with the IP address of the orange PI which provides the pages.
Note that the exchanges are done in http on the usual port 80 for the contents of pages. Ports 8001 to 8003 are used to exchange data with the Orange Pi responsible for reception. Ports 8004 to 8005 are used to exchange data with the Orange Pi responsible for transmission.
Customization of the installation
The image on Github is configured in English language, US keyboard and GMT time. Access the Orange Pi in ssh (user : root, password: remsdr) .
For an Orange Pi One Plus under Armbian type:
armbian-config
In the “Personal settings” section you can enter your preferences.
For an Orange Pi Zero 2 running Debian, apply the desired changes with the standard system instructions.
You can also access the Orange Pi in graphics mode using the chrome VNC extension.
ip address:5901
password: remsdr
All the sources are in the / var / www / html folder.
Cooling
If you use your Remote SDR application intensively, consider putting a heat sink on the CPU, in particular for the Orange Pi Zero 2. The CPU load rate is important: around 60%.
Also, I recommend a transmitter security system as described here.
Video on Remote SDR v2 installation
Posts describing Remote SDR
- Remote SDR V5 -Raspberry 4B or Orange Pi Image Installation
- Remote SDR v5 – Manual Installation
- Remote SDR v5
- QO-100 Satellite Live
- RTTY
- Troubleshooting
- QO-100 Transceiver
- SSTV
- WSJT-X – FT8
- Omnirig – Remote SDR
- Communication Ports
- Tone generators
- Setting of GPIO outputs
- Band Scanning
- Gains and Dynamics
- Frequencies Management
- Launch of Remote SDR
- CPU Cooling
- Web GUI
- Microphone and signal processing authorization
- Configurations
- Characteristics
- Introduction to Remote SDR
- Remote SDR – Audio Channels
- CW with Remote SDR
- Rotary Knob and Morse Manipulator for Remote SDR
- VHF and UHF NBFM Transceiver
- Remote SDR v4
- Gpredict — Remote SDR
- Remote SDR V4 – Raspberry Pi 4B or Orange Pi Zero 2 image installation
- Remote SDR v4 – Manual Installation
- SA818 – RTL-SDR
- Remote SDR – Examples of realization
- Transmit over QO-100 satellite with a Smartphone
- Remote SDR V2 – Software Architecture
- Remote SDR V1- Purchase
- Remote SDR V1 – Man Machine Interface
- Remote SDR V1 – Signal Processing
- Web Client to GNU Radio
- GNU Radio to Web client
- Remote SSB Transmitter
- Remote SSB Receiver
- GPIO on Orange PI One Plus H6
- TCXO installation on HackRF
- Q0-100 Transceiver with 2 SDR – Remote SDR V1








Thank you for your generous information and sharing via your website. Well done. I wish I was as capable.
Orange Pi have moved on with their development offerings and now have OPiZero3 boards available. Are there any images for OPiZero3 boards with the H618 uProcessors? Or alternately can an OS be applied (they can take Android12 TV, Debian 11 and 12, Ubuntu 20.04 and 22.04) and then a Remote SDR instal applied to that image?
Sorry,I have not yet moved to Opizero3. I am busy with a lot of projects.
Regards