RX Audio
Remote SDR has an audio channel for reception. The demodulation in AM, NBFM, WBFM, BLU or BLS is carried out by the signal processing installed on the Raspberry-Pi or the Orange-Pi. The signals are sent as 16-bit samples to the web browser.
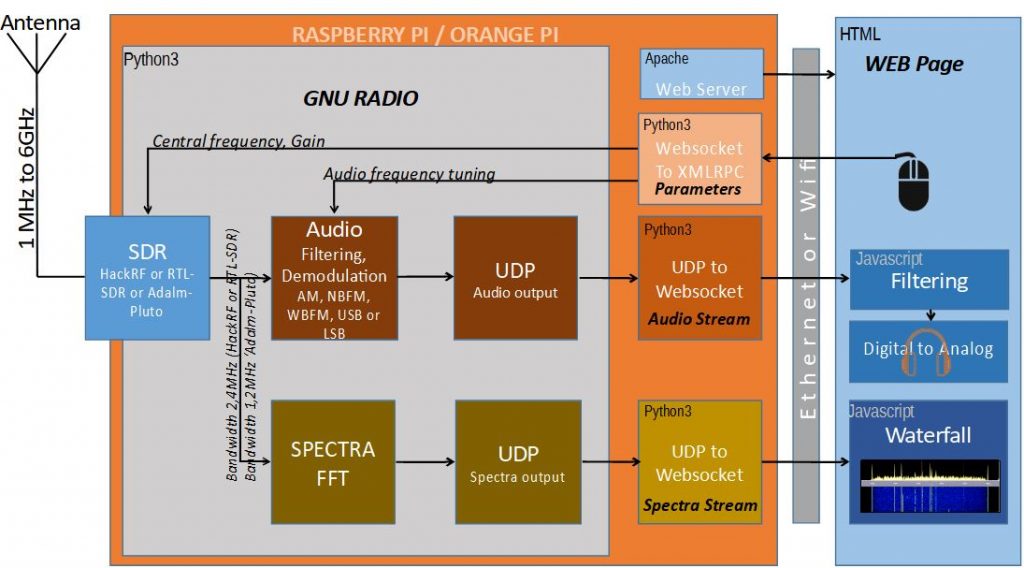
Locally, the browser performs various filters to limit the audio band, compensate for the spectrum or reduce noise. The interface offers many settings to adapt to the situation. There is also the option to go directly without filtering.
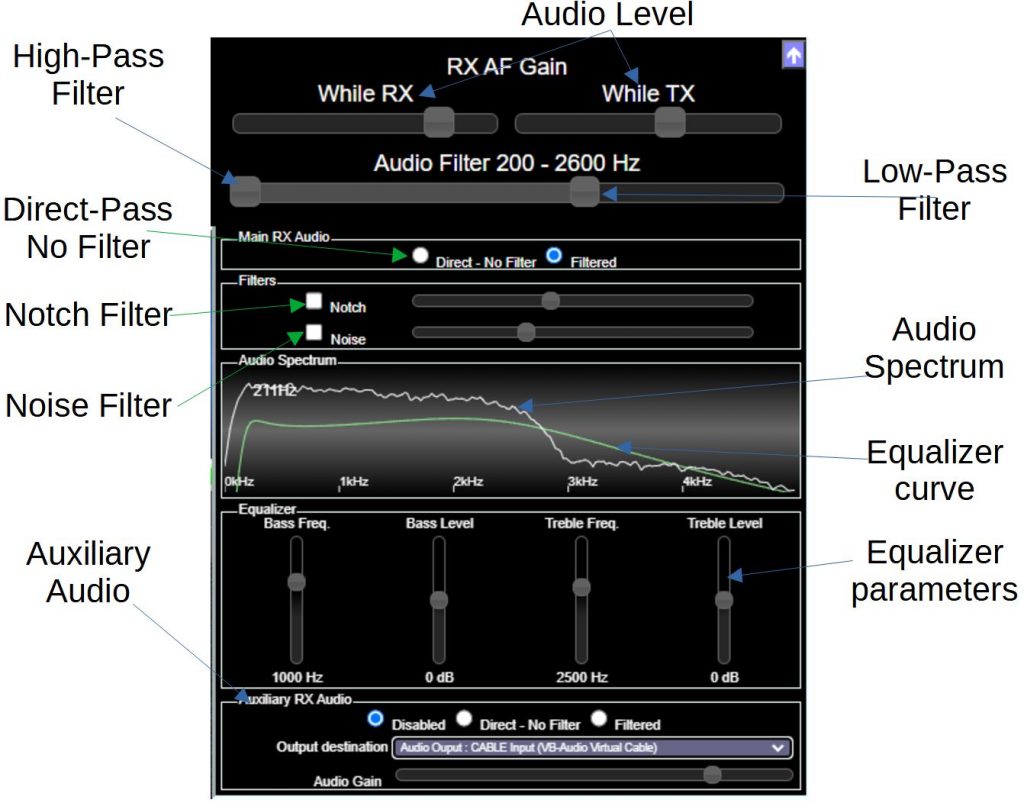
Since version 4.3 of Remote SDR, there is an additional output in parallel to be able to interface with software such as FT8 digital decoding or SSTV. In general, we go through a virtual audio cable found here: https://vb-audio.com/Cable/
Band filtering may or may not be applied to this auxiliary signal.
TX Audio
Remote SDR has an audio channel for transmission. The modulation in NBFM, BLU or BLS is carried out by the signal processing installed on the Raspberry-Pi or the Orange-Pi. At the level of the Web browser, it is possible to correct the spectrum to increase or decrease the bass or treble with an equalizer.
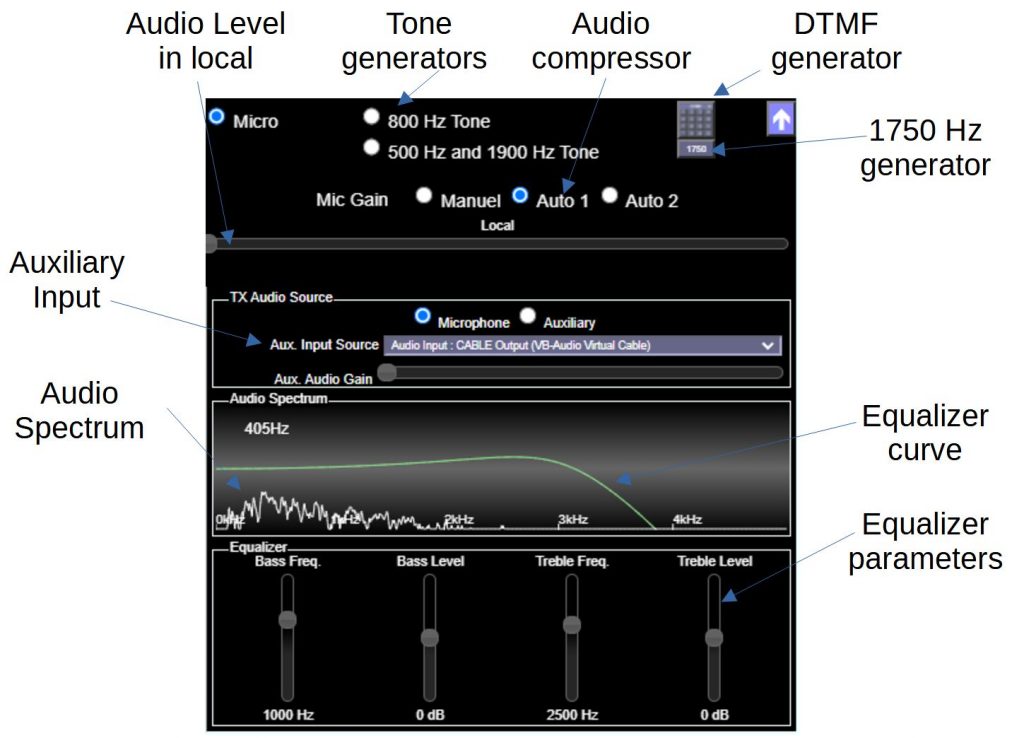
Instead of using the microphone, it is possible to send an auxiliary source. This is used for digital modes or SSTV that are injected through the Audio-Input virtual cable.
CW transmission
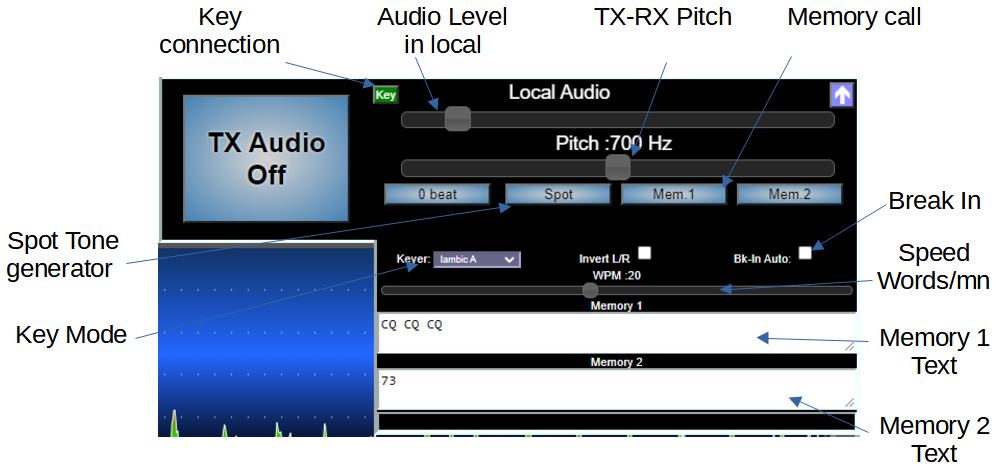
It is possible to transmit in CW mode using a manipulator connected to the USB input of the PC. The procedure is described here.
External control of Remote SDR
In general, if the auxiliary audio inputs are used for third-party software, it is necessary to control Remote SDR by this software to switch to transmission. Since version 4.3, Remote SDR has an Omnirig-compatible control interface that can be found described here: https://f1atb.fr/omnirig-remote-sdr-2/
Congrats on another great upgrade! And TY for 125!
Quick question – when I start up the TX bar is bright red. What does that indicate?
And the TXRX and RXTX buttons on the right of the bar – what are they for?
If my RX and TX don’t line up on a LEO and I am using Gpredict to adjust for doppler, what is the best procedure to shift the transmitter to get on the downlink receive frequency?
TY!
The TX bar is bright red when the frequency is out the defined band as it is defined in the configurationTX.js file
It is also bright red if you have linked the TX and RX frequencies and they are not coherent.
On the right TXRX and RXTX are only displayed if you don’t link the TX and RX frequencies. It allows to force the TX frequency to be equal to RX or reverse.
In the configuration file of RX and TX , you can define your preferred bands and the offset between the 2 in case of cross bands operations.
73