Obsolete. Go here now.
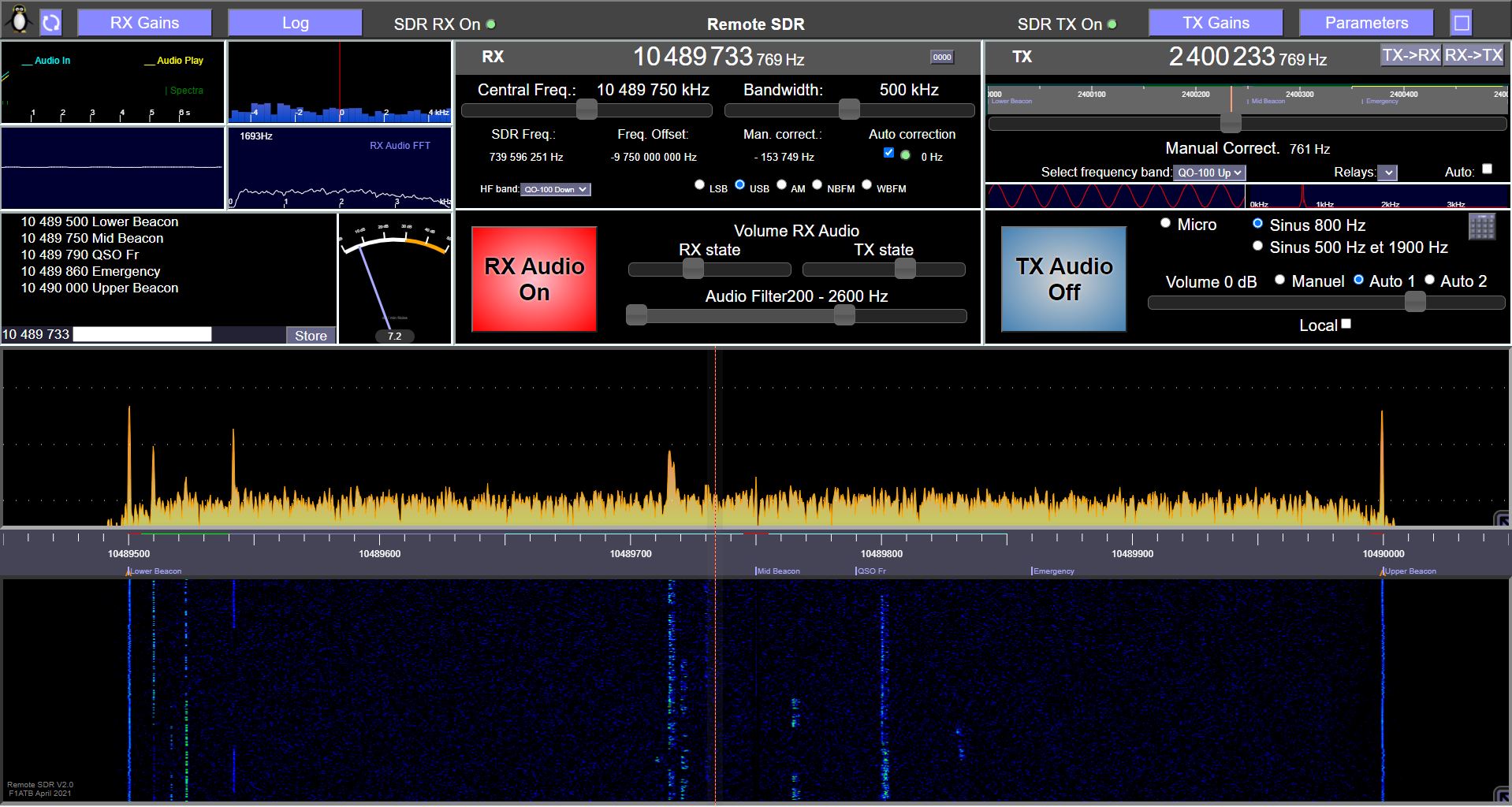
“Remote SDR” is a web application allowing to remotely control an amateur radio transceiver between 1 MHz and 6 GHZ. Its first application was the duplex control of a station allowing links to the geostationary satellite QO-100 / Es’Hail 2.
Version 2 offers new features:
- Processing of Adalm-Pluto SDR in addition to HackRF or RTL-SDR
- Reception in NBFM, WBFM, AM in addition to SSB
- Transmission in NBFM or SSB
- Spectral analysis on 2048 points instead of 1024.
- Transmitter modulation compressor
- CTCSS encoder
- DTMF encoder
- Programmable frequency shift for relays
The set is made up of:
- a reception channel: SDR (Software Design Radio)
- a transmission channel: SDR
- one or 2 Orange PI or Raspberry Pi 4 single board computer for signal processing and web server
- from a PC, a tablet, or even a smartphone, controlling everything with “Remote SDR” running on a web browser like Chrome or Edge.
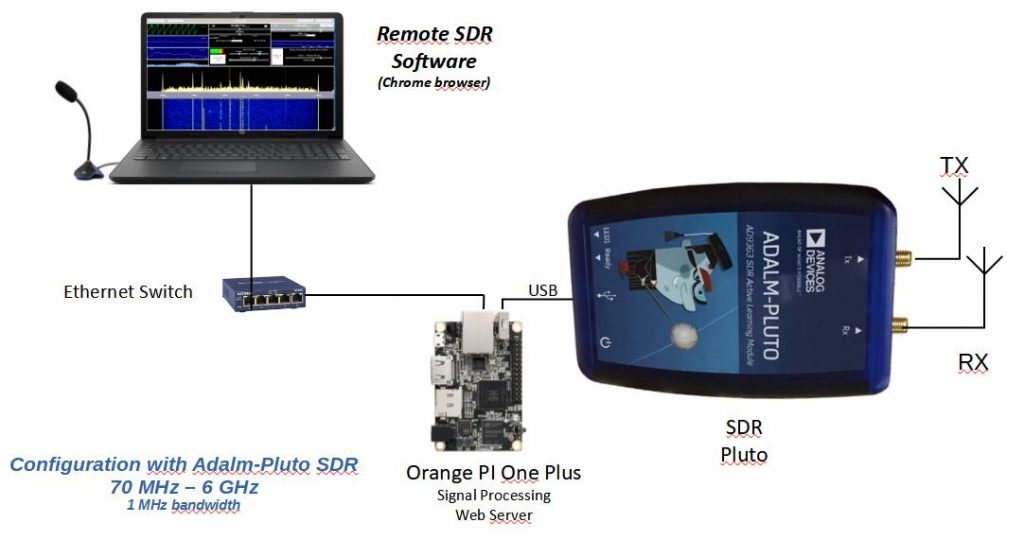
COMPACT CONFIGURATION WITH AN ADALM-PLUTO – OPI One plus – ETHERNET
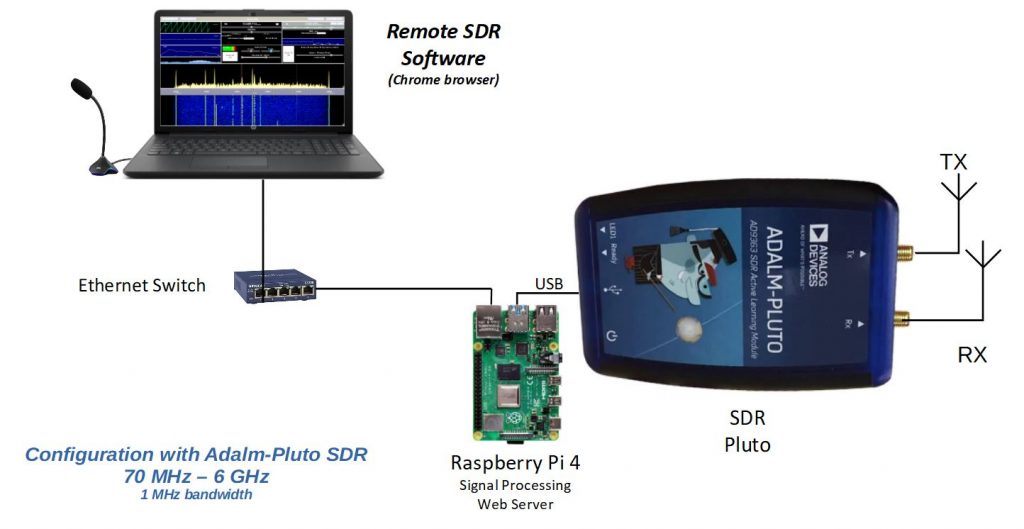
COMPACT CONFIGURATION WITH AN ADALM-PLUTO – Raspberry 4 – ETHERNET
COMPACT CONFIGURATION WITH AN ADALM-PLUTO – OPI ZERO 2 – WIFI
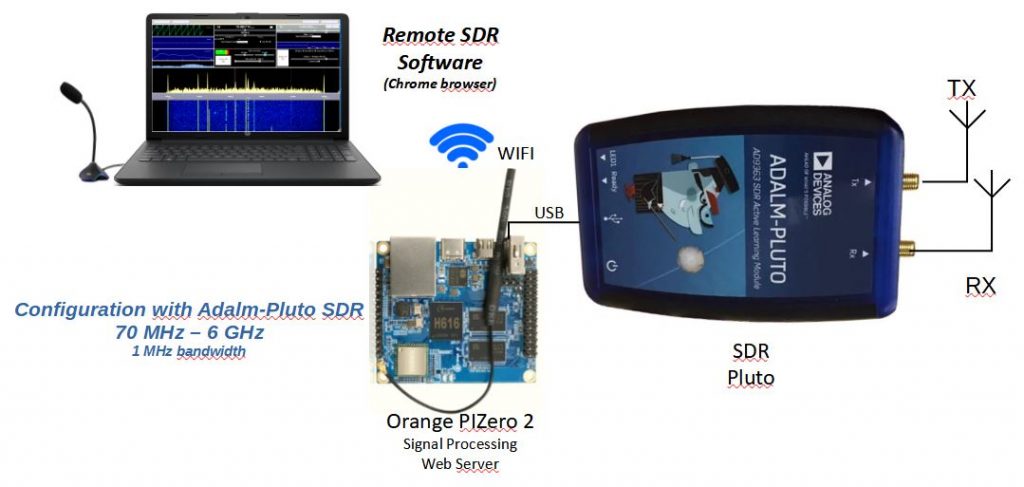
Interesting solution with the new Orange Pi Zero 2 which allows a WIFI connection to the HF part
MIXED HACKRF AND RTL-SDR CONFIGURATION – Raspberry pi 4
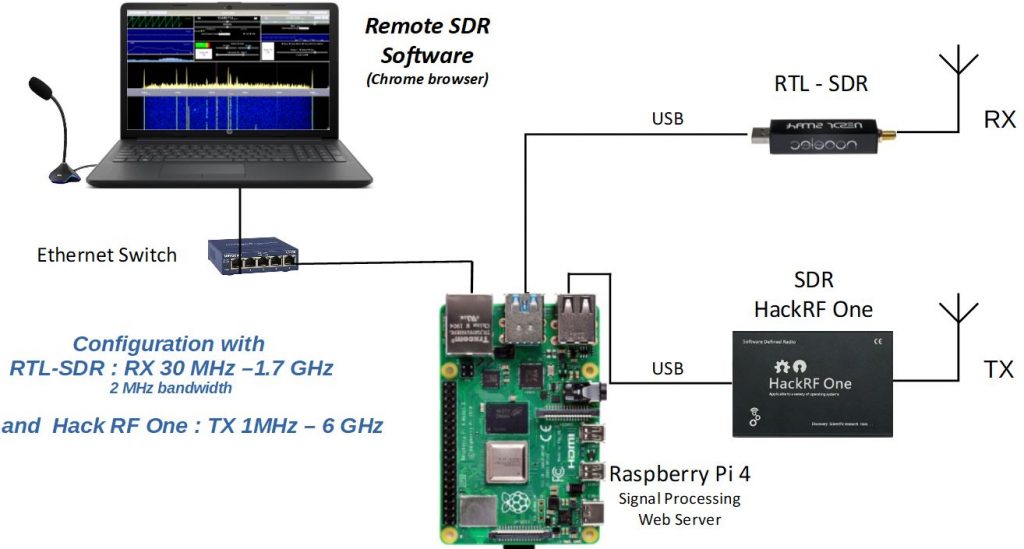
CONFIGURATION 2 HACK RF ONE
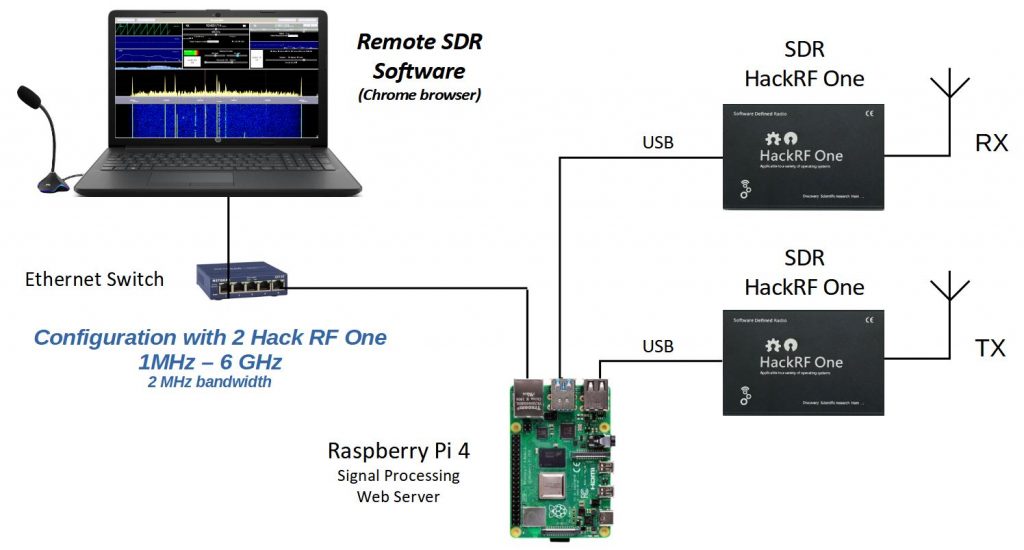
These configurations make it possible to locate the HF part near the antennas, which is essential for links above GHz. In the transmission chain, amplifiers must be added to bring the HF signal to the desired level as well as filtering to ensure that unwanted lines are not emitted. The SDR of the reception chain can be either an RF Hack, an RTL-SDR or a Pluto depending on the frequency band you want to cover. Not all RTL-SDR models cover the same band. The transmission reception is carried out in full-duplex which is essential during satellite connection to hear the return of its own signal.
The “Orange Pi” are processors similar to the Raspberry Pi running under the Armbian or Debian Operating System. In 2020 I used the Orange Pi One Plus, now in 2021 the Orange Pi Zero 2 also offers a 64-bit / 4-core processor, but also an ethernet or WiFi connection. They serve as a web server and perform radio signal processing. In all the configurations presented above, you can use an Orange Pi One Plus or the recent Orange Pi Zero 2.
Note: it seems that as of this day (July 2021), the Orange Pi One Plus is no longer on sale. The Orange Pi Zero 2 remains available and replace perfectly the Orange Pi One Plus. The Raspberry Pi 4 with a 2 GB memory is a good alternative.
Example Transceiver QO-100
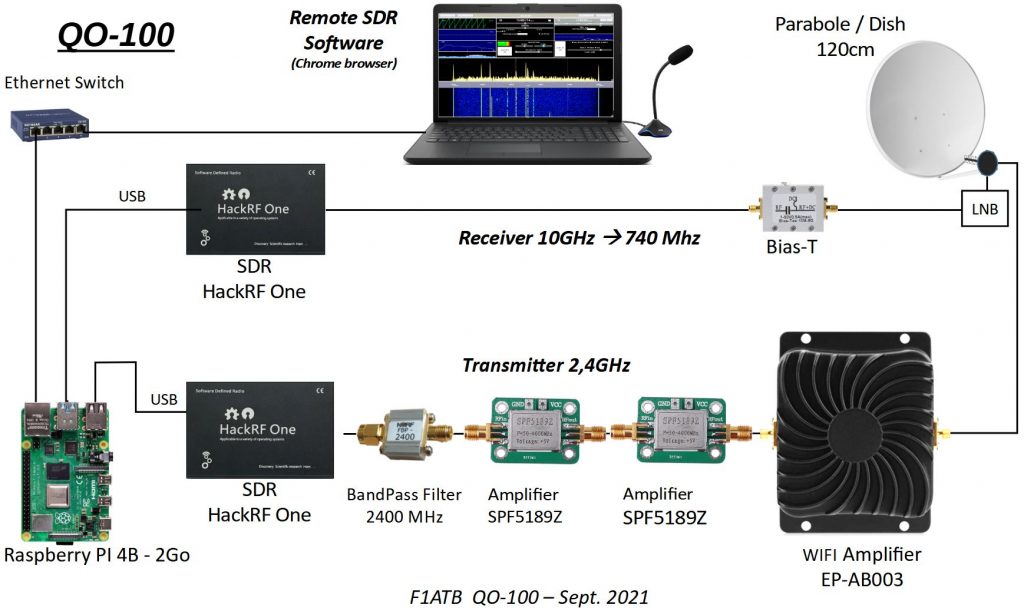
Example UHF Transceiver – Wifi – Orange Pi Zero 2
New configuration with the Orange Pi Zero 2 which allows communication via WIFI. No more wired Ethernet connection, only 220v near the transceiver.
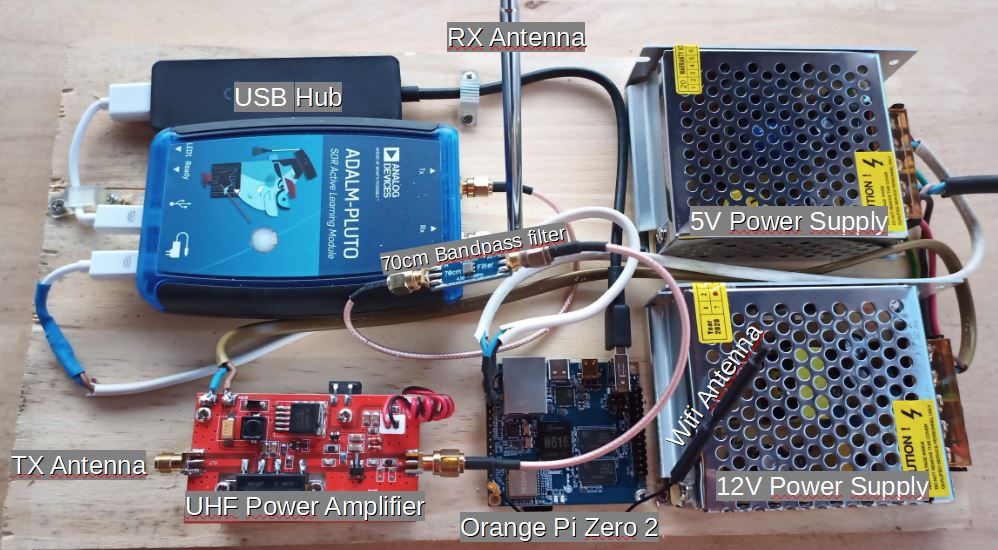
Note , you need a USB hub between the Pluto and the Orange PI One Plus (not for the Orange Pi Zero 2). This corresponds to a system bug that I cannot explain.
Key points of Remote SDR
In addition to being able to locate the HF treatment near the antennas, other points should be noted such as:
Data Flow reduction
An SDR like the Pluto requires 1.4 M samples / s (minimum) * 2 Bytes (16 bits) * 2 channels (I and Q) = 5.6 M Bytes / s for reception. The same for the transmission. Which gives us more than 10M bytes / second.
With Remote SDR, the output on Ethernet or in Wifi requires:
- 10 k samples / s * 2 bytes for the receiver audio
- 10.24 k sample / s * 2 bytes for the receiver spectrum
- 10 k samples / s * 2 bytes for transmiter audio
We are at less than 100 k bytes / s by adding the control data.
There is therefore a reduction of approximately 100 in the communication flow required, which facilitates remote control via internet / ethernet without loss of quality through data compression.
The mini remote computer

Indeed, we have a remote computer which has a GPIO to which it is possible to add functions. For example, controlling an antenna rotor, measuring electrical voltages, temperatures, etc.. It is possible to access the system via the web (Apache server), in SSH to launch an application in terminal mode, or in graphical mode by desktop and VNC.
Source Code and Image
The source code and the image for an Orange Pi One Plus are available on Github https://github.com/F1ATB/Remote-SDR .
Posts describing Remote-SDR
- Remote SDR V5 -Raspberry 4B or Orange Pi Image Installation
- Remote SDR v5 – Manual Installation
- Remote SDR v5
- QO-100 Satellite Live
- RTTY
- Troubleshooting
- QO-100 Transceiver
- SSTV
- WSJT-X – FT8
- Omnirig – Remote SDR
- Communication Ports
- Tone generators
- Setting of GPIO outputs
- Band Scanning
- Gains and Dynamics
- Frequencies Management
- Launch of Remote SDR
- CPU Cooling
- Web GUI
- Microphone and signal processing authorization
- Configurations
- Characteristics
- Introduction to Remote SDR
- Remote SDR – Audio Channels
- CW with Remote SDR
- Rotary Knob and Morse Manipulator for Remote SDR
- VHF and UHF NBFM Transceiver
- Remote SDR v4
- Gpredict — Remote SDR
- Remote SDR V4 – Raspberry Pi 4B or Orange Pi Zero 2 image installation
- Remote SDR v4 – Manual Installation
- SA818 – RTL-SDR
- Remote SDR – Examples of realization
- Transmit over QO-100 satellite with a Smartphone
- Remote SDR V2 – Software Architecture
- Remote SDR V1- Purchase
- Remote SDR V1 – Man Machine Interface
- Remote SDR V1 – Signal Processing
- Web Client to GNU Radio
- GNU Radio to Web client
- Remote SSB Transmitter
- Remote SSB Receiver
- GPIO on Orange PI One Plus H6
- TCXO installation on HackRF
- Q0-100 Transceiver with 2 SDR – Remote SDR V1
Pingback: Remote SDR v2 | European Hamradio CQ portal
Pingback: Tech Minds: Remote SDR V2 with Orange Pi and Transmit Capable
Fantastic system, very reliable and simple to be in the air via QO100 with great reliability and excellent quality, the man-machine interface is very intuitive and fast to operate, congratulations for the excellent design.
Thank you. Have fun with your installation. I will add new features in the coming months.
I built it, it works very well. All that I could not figure out how to enable the CTCSS encoder for TX. Any suggestion is very welcome.
Béla, good remark,I have updated the Tips page to explain you can set the CTCSS in the configurationTX.js file
Pingback: Installing Remote SDR V2 on a Raspberry Pi 4B
I am wondering if a mixed setup could be used for Amsat LEO birds? (144/435) Would need inverting transponder support and some type of freq. tracking to easily support Doppler.
TY!
…or allow frequency control from Gpredict.
First, a mixed setup, 144/432 MHz works perfectly with RemoteSDR.
To invert USB/LSB for a transponder, I put it on my To Do list for a next release.
For the tracking in frequency, I have to think of it to find a good solution.
73
F1ATB
The inversion LSB/USB between RX and TX is available now in version 2.5
Hi doe this osftware support the Pluto Plus? Is so does it support the 20Mhz bandwidth?
No it does’nt support Pluto Plus. 73
Pingback: Adalm Pluto Remote ??? – DARC OV H05
Awesome development. I’m inspired to write GNU Radio decoders.
Is there an opportunity to support LimeSDR and Ettus USRP SDR?
It would also be great for the system to be able to connect to an existing SoapySDR Server.
Does it have to be on a Pi, or will it compile on an x86 system?
Thanks!
For the moment only on Raspberry Pi 4B or Orange Pi Zero 2.
73
How to change tx settings like 27mhz /11m
In the 2 configuration files, configurationRX.js and configurationTX.js, you can define your prefered bands.
Pingback: SDR Web GUI | SHEN XIAODONG'S BLOG
Now (September 2022) Remote SDR exits in version 5.07
Upgrade your description.
Regards
André
Pingback: Homepage